Current issue
About the Journal
Scientific Council
Editorial Board
Regulatory and archival policy
Code of publishing ethics
Publisher
Information about the processing of personal data in relation to cookies and newsletter subscription
Archive
For Authors
For Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
Links
Sklep Wydawnictwa SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Privacy policy
Accessibility statement
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
The role of cortisol in etiology and treatment of bruxism – a literature review
1
Students’ Scientific Club, Department of Temporomandibular Disorders, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
2
Department of Temporomandibular Disorders, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Corresponding author
Wiktoria Galińska
Studenckie Koło Naukowe, Katedra i Zakład Dysfunkcji Narządu Żucia, pl. Traugutta 2, 41-800 Zabrze
Studenckie Koło Naukowe, Katedra i Zakład Dysfunkcji Narządu Żucia, pl. Traugutta 2, 41-800 Zabrze
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2025;79:1-7
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
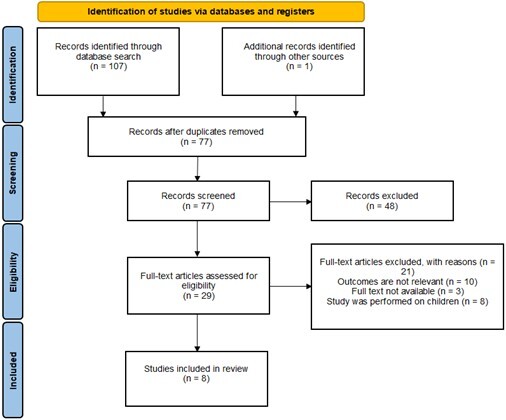
The aim of the study was to analyze the role of cortisol in both the treatment and etiology of bruxism. A literature review was conducted using the PubMed and Embase databases, focusing on publications from November 2013 to November 2023, with no language restrictions. The titles and abstracts were initially screened, followed by a full-text selection process. Observational studies and randomized controlled trials that assessed the relationship between diagnosed bruxism and salivary cortisol levels were included in the analysis. Methodological quality assessment and data extraction were performed on the included studies. Ultimately, eight articles were included in the review. The analysis revealed a significant correlation between higher cortisol concentrations and the occurrence of bruxism. Moreover, individuals with bruxism exhibited higher cortisol concentrations before the initiation of treatment compared to the post-treatment levels.
REFERENCES (23)
1.
Musiała N., Hołyńska-Iwan I., Olszewska-Słonina D. Cortisol – inspection in the physiology and stress. [Article in Polish]. Diagn. Lab. 2018; 54(1): 29–36, doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0013.7553.
2.
Kuo T., McQueen A., Chen T.C., Wang J.C. Regulation of glucose homeostasis by glucocorticoids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015; 872: 99–126, doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2895-8_5.
3.
Exton J.H. Regulation of gluconeogenesis by glucocorticoids. Monogr. Endocrinol. 1979; 12: 535–546, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81265-1_28.
4.
Załuska M., Janota B. Dehydroepiandrosteron (DHEA) in the mechanisms of stress and depression. [Article in Polish]. Psychiatr. Pol. 2009; 43(3): 263–274.
5.
McEwen B.S., Angulo J., Cameron H., Chao H.M., Daniels D., Gannon M.N. et al. Paradoxical effects of adrenal steroids on the brain: protection versus degeneration. Biol. Psychiatry 1992; 31(2): 177–199, doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(92)90204-d.
6.
Więckiewicz M., Służalec K., Więckiewicz W. Influence of stress on the development of bruxism in the light of contemporary medical knowledge. [Article in Polish]. Mag. Stomat. 2011; 21(2): 34–37.
7.
Lobbezoo F., Ahlberg J., Glaros A.G., Kato T., Koyano K., Lavigne G.J. et al. Bruxism defined and graded: an international consensus. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2013; 40(1): 2–4, doi: 10.1111/joor.12011.
8.
De Meyer M.D., De Boever J.A. The role of bruxism in the appearance of temporomandibular joint disorders. [Article in French]. Rev. Belge Med. Dent. (1984) 1997; 52(4): 124–138.
9.
Manfredini D., Winocur E., Guarda-Nardini L., Paesani D., Lobbezoo F. Epidemiology of bruxism in adults: a systematic review of the literature. J. Orofac. Pain 2013; 27(2): 99–110, doi: 10.11607/jop.921.
10.
Kanathila H., Pangi A., Poojary B., Doddamani M. Bruxism and its management. Int. J. Appl. Dent. Sci. 2018; 4(1): 290–295.
11.
Macaluso G.M., Guerra P., Di Giovanni G., Boselli M., Parrino L., Terzano M.G. Sleep bruxism is a disorder related to periodic arousals during sleep. J. Dent. Res. 1998; 77(4): 565–573, doi: 10.1177/00220345980770040901.
12.
Gonçalves L.P.V., Toledo O.A., Otero S.A.M. The relationship between bruxism, occlusal factors and oral habits. Dental Press J. Orthod. 2010; 15(2): 97–104.
13.
Oliveira M.T., Bittencourt S.T., Marcon K., Destro S., Pereira J.R. Sleep bruxism and anxiety level in children. Braz. Oral Res. 2015; 29: S1806-83242015000100221, doi: 10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2015.vol29.0024.
14.
Renner A.C., da Silva A.A., Rodriguez J.D., Simões V.M., Barbieri M.A., Bettiol H. et al. Are mental health problems and depression associated with bruxism in children? Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2012; 40(3): 277–287, doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2011.00644.x.
15.
Bayar G.R., Tutuncu R., Acikel C. Psychopathological profile of patients with different forms of bruxism. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012; 16(1): 305–311, doi: 10.1007/s00784-010-0492-9.
16.
Fluerașu M.I., Bocsan I.C., Buduru S., Pop R.M., Vesa S.C., Zaharia A. et al. The correlation between sleep bruxism, salivary cortisol, and psychological status in young, Caucasian healthy adults. Cranio 2021; 39(3): 218–224, doi: 10.1080/08869634.2019.1619250.
17.
Karakoulaki S., Tortopidis D., Andreadis D., Koidis P. Relationship between sleep bruxism and stress determined by saliva biomarkers. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015; 28(5): 467–474, doi: 10.11607/ijp.4296.
18.
Rosar J.V., Marquezin M.C.S., Pizzolato A.S., Kobayashi F.Y., Bussadori S.K., Pereira L.J. et al. Identifying predictive factors for sleep bruxism severity using clinical and polysomnographic parameters: a principal component analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021; 17(5): 949–956, doi: 10.5664/jcsm.9078.
19.
Miletić A., Lazić Z., Todorović A., Đorđević I., Popović D., Lazić V. Stress assessment in patients with clinically diagnosed sleep bruxism. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2018; 75(10): 1014–1019, doi: 10.2298/VSP160902029M.
20.
Khayamzadeh M., Mirzaii-Dizgah I., Aghababainejad P., Habibzadeh S., Kharazifard M.J. Relationship between parafunctional habits and salivary biomarkers. Front. Dent. 2019; 16(6): 465–472, doi: 10.18502/fid.v16i6.3446.
21.
Salameh E., Alshaarani F., Hamed H.A., Nassar J.A. Investigation of the relationship between psychosocial stress and temporomandibular disorder in adults by measuring salivary cortisol concentration: A case-control study. J. Indian. Prosthodont. Soc. 2015; 15(2): 148–152, doi: 10.4103/0972-4052.158075.
22.
Rosar J.V., Barbosa T.S., Dias I.O.V., Kobayashi F.Y., Costa Y.M., Gavião M.B.D. et al. Effect of interocclusal appliance on bite force, sleep quality, salivary cortisol levels and signs and symptoms of temporomandibular dysfunction in adults with sleep bruxism. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017; 82: 62–70, doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.05.018.
23.
Al-Oudah G.A., AL-Ameedee A.H., AL-Ameedee A.A. Effect of chlordiazepoxide oral tablet on oral recurrent bruxism: a clinical trial human study. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2021; 12(1): 921–924, doi: 10.31838/srp.2021.1.128.
The Medical University of Silesia in Katowice, as the Operator of the annales.sum.edu.pl website, processes personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about Users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms, saving cookies in end devices, as well as by collecting web server logs, which are in the possession of the website Operator. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services in accordance with the Privacy policy.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.