Current issue
About the Journal
Scientific Council
Editorial Board
Regulatory and archival policy
Code of publishing ethics
Publisher
Information about the processing of personal data in relation to cookies and newsletter subscription
Archive
For Authors
For Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
Links
Sklep Wydawnictwa SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Privacy policy
Accessibility statement
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
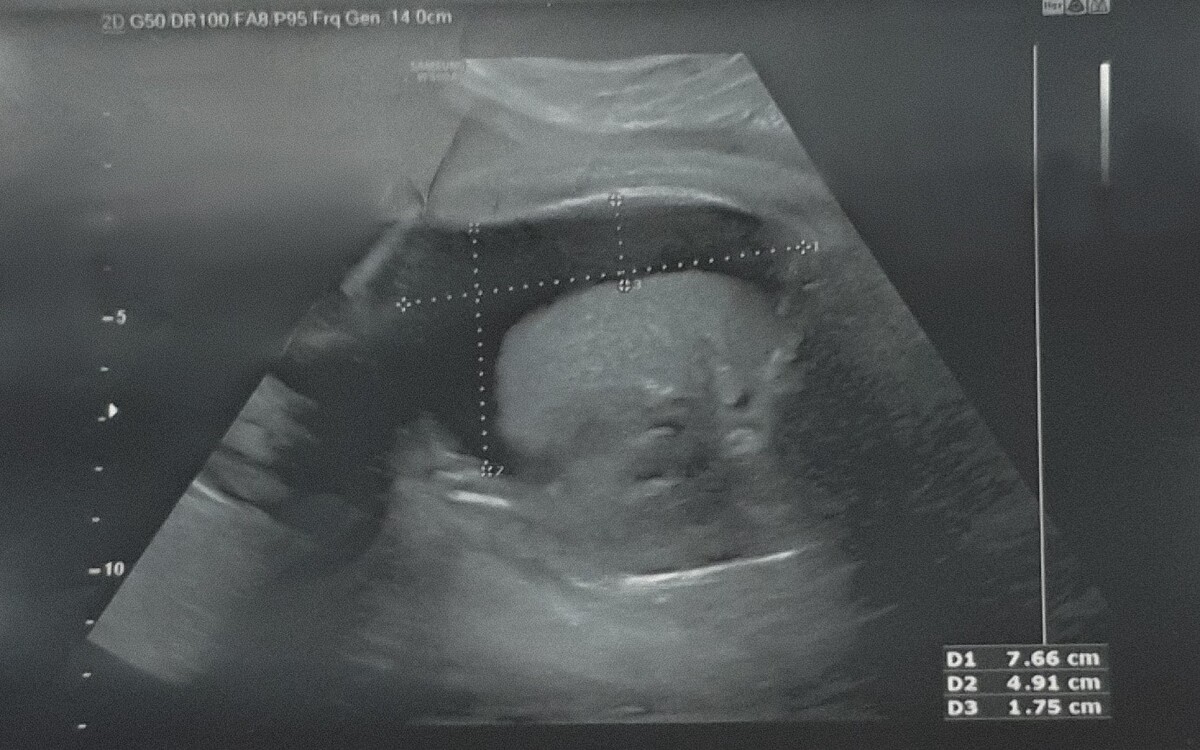
A case of COVID-19 in pregnancy complicated by fetal pleural effusion
1
Department of Gynaecology, Obstetrics and Oncological Gynaecology, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Corresponding author
Natalia Filochowska
Katedra i Oddział Kliniczny Ginekologii, Położnictwa i Ginekologii Onkologicznej, ul. Stefana Batorego 15, 41-902 Bytom
Katedra i Oddział Kliniczny Ginekologii, Położnictwa i Ginekologii Onkologicznej, ul. Stefana Batorego 15, 41-902 Bytom
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2024;78:89-93
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which can lead to severe respiratory failure, has become a real threat to pregnancy. Although vertical transmission of the virus through the placenta appears to be rare, there is increasing evidence that a SARS-CoV-2 infection may cause complications during pregnancy. We report a case of COVID-19 in a pregnancy complicated by fetal pleural effusion in the third trimester of pregnancy. To our knowledge, only 4 similar cases have been reported to date. A 29-year-old woman in the 37th week of pregnancy admitted to the department of pregnancy pathology due to right fetal pleural effusion. In the 34th week of pregnancy, the patient suffered from COVID-19 with symptoms of fever and general weakness. The infection was confirmed by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). At 38 weeks, vaginal delivery occurred. The male newborn with a 6/7/8 point Apgar score required continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) breathing assistance and was transferred to the intensive care unit. The rapid antigen test was negative. The ultrasound showed collapse of the right lung compressed by fluid in the pleural cavity. Inflammation, congenital TORCH and group B Coxsackie virus infection, chromosomal disorders and anatomical defects were excluded. During hospitalization 850 ml of lymphatic fluid was drained. We suspect a possible causal relationship between non-immune fetal hydrops and coronavirus disease.
FUNDING
No funding was received to conduct the study.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES (19)
1.
Schwartz D.A. An analysis of 38 pregnant women with COVID-19, their newborn infants, and maternal-fetal transmission of SARS-CoV-2: maternal coronavirus infections and pregnancy outcomes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020; 144(7): 799–805, doi: 10.5858/arpa.2020-0901-SA.
2.
Shende P., Gaikwad P., Gandhewar M., Ukey P., Bhide A., Patel V. et al. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in the first trimester placenta leading to transplacental transmission and fetal demise from an asymptomatic mother. Hum. Reprod. 2021; 36(4): 899–906, doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa367.
3.
Rodrigues M.L., Gasparinho G., Sepúlveda F., Matos T. Signs suggestive of congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection with intrauterine fetal death: A case report. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021; 256: 508–509, doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.11.042.
4.
Pilarska I., Bizon M., Sawicki W. Influence of COVID-19 infection on placental function. Ginekol. Pol. 2023; 94(1): 79–83, doi: 10.5603/GP.a2022.0139.
5.
Kumar D., Verma S., Mysorekar I.U. COVID-19 and pregnancy: clinical outcomes; mechanisms, and vaccine efficacy. Transl. Res. 2023; 251: 84–95, doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.08.007.
6.
Patanè L., Morotti D., Giunta M.R., Sigismondi C., Piccoli M.G., Frigerio L. et al. Vertical transmission of coronavirus disease 2019: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 RNA on the fetal side of the placenta in pregnancies with coronavirus disease 2019–positive mothers and neonates at birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020; 2(3): 100145, doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100145.
7.
Oncel M.Y., Akın I.M., Kanburoglu M.K., Tayman C., Coskun S., Narter F. et al. A multicenter study on epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 125 newborns born to women infected with COVID-19 by Turkish Neonatal Society. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021; 180(3): 733–742, doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03767-5.
8.
Gubbari C., Govindarajan V., Reddy C., Raman P., Supriya M. Newborn with nonimmune hydrops secondary to fetal COVID-19 Myocarditis. Indian J. Pediatr. 2022; 89(1): 99, doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03950-y.
9.
Popescu D.E., Cioca A., Muresan C., Navolan D., Gui A., Pop O. et al. A case of COVID-19 pregnancy complicated with hydrops fetalis and intrauterine death. Medicina (Kaunas) 2021; 57(7): 667, doi: 10.3390/medicina57070667.
10.
Hsu A.L., Guan M., Johannesen E., Stephens A.J., Khaleel N., Kagan N. et al. Placental SARS‐CoV‐2 in a pregnant woman with mild COVID‐19 disease. J. Med. Virol. 2021; 93(2): 1038–1044, doi: 10.1002/jmv.26386.
11.
Baud D., Greub G., Favre G., Gengler C., Jaton K., Dubruc E. et al. Second-trimester miscarriage in a pregnant woman with SARS-CoV-2 infection. JAMA 2020; 323(21): 2198–2200, doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.7233.
12.
Kiappe O.P., Santos da Cruz N.F., Rosa P.A.C., Arrais L., Bueno de Moraes N.S. Ocular assessments of a series of newborns gestationally exposed to maternal COVID-19 infection. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021; 139(7): 777–780, doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.1088.
13.
Krasniqi F., Pistulli E., Gashi A.M., Krasniqi I. Non-immunologic hydrops fetalis and coronavirus disease (COVID-19) – A case report. Ro. J. Pediatr. 2021; 70(1): 75–79, doi: 10.37897/RJP.2021.1.14.
14.
Bellini C., Hennekam R.C.M., Fulcheri E., Rutigliani M., Morcaldi G., Boccardo F. et al. Etiology of nonimmune hydrops fetalis: a systematic review. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2009; 149A(5): 844–851, doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32655.
15.
Lima A.R.O., Cardoso C.C., Bentim P.R.B., Voloch C.M., Rossi Á.D., da Costa R.M.M.S.C. et al. Maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection associated to systemic inflammatory response and pericardial effusion in the newborn: a case report. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021; 10(4): 536–539, doi: 10.1093/jpids/piaa133.
16.
Zeng H., Xu C., Fan J., Tang Y., Deng Q., Zhang W. et al. Antibodies in infants born to mothers with COVID-19 pneumonia. JAMA 2020; 323(18): 1848–1849, doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4861.
17.
Yang H., Sun G., Tang F., Peng M., Gao Y., Peng J. et al. Clinical features and outcomes of pregnant women suspected of coronavirus disease 2019. J. Infect. 2020; 81(1): e40–e44, doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.003.
18.
Askary E., Poordast T., Shiravani Z., Ali M.A., Hashemi A., Naseri R. et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) manifestations during pregnancy in all three trimesters: A case series. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2021; 19(2): 191–204, doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v19i2.8477.
19.
Kyle M.H., Glassman M.E., Khan A., Fernández C.R., Hanft E., Emeruwa U.N. et al. A review of newborn outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Semin. Perinatol. 2020; 44(7): 151286, doi: 10.1016/j.semperi.2020.151286.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
The Medical University of Silesia in Katowice, as the Operator of the annales.sum.edu.pl website, processes personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about Users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms, saving cookies in end devices, as well as by collecting web server logs, which are in the possession of the website Operator. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services in accordance with the Privacy policy.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.