Current issue
About the Journal
Scientific Council
Editorial Board
Regulatory and archival policy
Code of publishing ethics
Publisher
Information about the processing of personal data in relation to cookies and newsletter subscription
Archive
For Authors
For Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
Links
Sklep Wydawnictwa SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Privacy policy
Accessibility statement
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
Cystic lymphangioma of the greater omentum coexisting with groin hernia in 2-year-old girl, mimicking intra-abdominal fluid with Nuck’s canal hydrocele
1
Department of Children’s Developmental Defects Surgery and Traumatology, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
2
DiaMMed, Nowy Targ, Poland
Corresponding author
Michał Pasierbek
Klinika Chirurgii Wad Rozwojowych Dzieci i Traumatologii, Wydział Nauk Medycznych w Zabrzu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, ul. 3 Maja 13–15, 41-800 Zabrze
Klinika Chirurgii Wad Rozwojowych Dzieci i Traumatologii, Wydział Nauk Medycznych w Zabrzu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, ul. 3 Maja 13–15, 41-800 Zabrze
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2025;79:201-205
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Lymphatic cysts are congenital malformations that predominantly occur in the head and neck region. Intra-abdominal lesions are rare and may be present in the mesentery, retroperitoneal space, and greater omentum. When a cyst in the abdominal cavity is suspected, ultrasonography is the diagnostic procedure of choice. Radical resection, if feasible, is the preferred treatment, as incomplete excision can lead to recurrence. However, for lesions located in the mesentery and retroperitoneal space, aspiration with the administration of obliterating agents may be a better approach than surgical treatment. In recent years, laparoscopy has become a favorable alternative to laparotomy.
Case report:
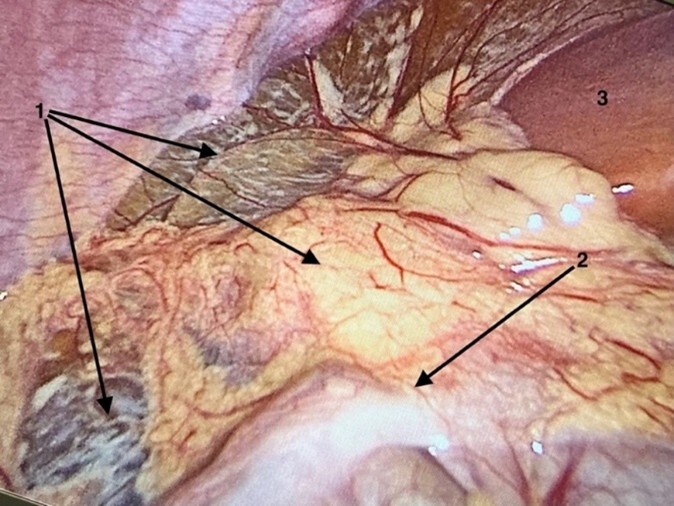
A 2-year-old girl was referred for surgery due to the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity along with a coexisting right-sided hydrocele of the canal of Nuck. During the surgical procedure, a large multilocular lesion originating from the greater omentum and extending into the hernia sac of a right inguinal hernia was identified. The cyst was resected laparoscopically, and the inguinal hernia was repaired. Histopathological examination confirmed a lymphatic cyst.
Conclusions:
Laparoscopic resection is a safe method for treating a large lymphatic cyst of the greater omentum.
Lymphatic cysts are congenital malformations that predominantly occur in the head and neck region. Intra-abdominal lesions are rare and may be present in the mesentery, retroperitoneal space, and greater omentum. When a cyst in the abdominal cavity is suspected, ultrasonography is the diagnostic procedure of choice. Radical resection, if feasible, is the preferred treatment, as incomplete excision can lead to recurrence. However, for lesions located in the mesentery and retroperitoneal space, aspiration with the administration of obliterating agents may be a better approach than surgical treatment. In recent years, laparoscopy has become a favorable alternative to laparotomy.
Case report:
A 2-year-old girl was referred for surgery due to the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity along with a coexisting right-sided hydrocele of the canal of Nuck. During the surgical procedure, a large multilocular lesion originating from the greater omentum and extending into the hernia sac of a right inguinal hernia was identified. The cyst was resected laparoscopically, and the inguinal hernia was repaired. Histopathological examination confirmed a lymphatic cyst.
Conclusions:
Laparoscopic resection is a safe method for treating a large lymphatic cyst of the greater omentum.
REFERENCES (12)
1.
Mohite P.N., Bhatnagar A.M., Parikh S.N. A huge omental lymphangioma with extention into labia majorae: a case report. BMC Surg. 2006; 6: 18, doi: 10.1186/1471-2482-6-18.
2.
Makni A., Chebbi F., Fetirich F., Ksantini R., Bedioui H., Jouini M. et al. Surgical management of intra‐abdominal cystic lymphangioma. Report of 20 cases. World J. Surg. 2012; 36(5): 1037–1043, doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1515-2.
3.
Hamaguchi Y., Arita S., Sugimoto N., Inamoto O., Takagi H., Kogire M. et al. Laparoscopic resection of abdominal cystic lymphangioma derived from lesser omentum: case report. Medicine 2020; 99(1): e18641, doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018641.
4.
Takeda A., Ito H., Nakamura H. Large omental cystic lymphangioma masquerading as mucinous ovarian neoplasia in an 8-year-old premenarchal girl: The findings from diagnostic imaging and laparoscopic-assisted excision. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2017; 30(6): 659–662, doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2017.06.003.
5.
Riahinezhad M., Sarrami A.H., Shariat Z., Taghizadeh F. Two unusual sites of cystic lymphangioma in a child: A report of imaging profile with surgical and histopathologic findings. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2015; 4: 169, doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.162546.
6.
Luo C.C., Huang C.S., Chao H.C., Chu S.M., Hsueh C. Intra-abdominal cystic lymphangiomas in infancy and childhood. Chang Gung Med. J. 2004; 27(7): 509–514.
7.
Dongare P.A., Bhaskar S.B., Harsoor S.S., Garg R., Kannan S., Goneppanavar U. et al. Perioperative fasting and feeding in adults, obstetric, paediatric and bariatric population: Practice Guidelines from the Indian Society of Anaesthesiologists. Indian J. Anaesth. 2020; 64(7): 556–584, doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_735_20.
8.
Walker A.R., Putnam T.C. Omental, mesenteric, and retroperitoneal cysts: a clinical study of 33 new cases. Ann. Surg. 1973; 178(1): 13–19, doi: 10.1097/00000658-197307000-00003.
9.
Nam S.H., Kim D.Y., Kim S.C., Kim I.K. The surgical experience for retroperitoneal, mesenteric and omental cyst in children. J. Korean Surg. Soc. 2012; 83(2): 102–106, doi: 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.2.102.
10.
Tsopozidi M., Kepertis C., Godosis D., Mouravas V., Demiri C., Spyridakis I. Laparoscopic-assisted excision of a huge polycystic omental lymphangioma in a 3 year old patient presenting with acute abdomen: case report and review. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021; 38: 228, doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.38.228.26607.
11.
Sadecka A.I., Wolski M. Major complication caused by inguinal hernia recurrence after percutaneous internal ring suturing procedure in a patient with Loeys-Dietz syndrome: a case report. Cureus 2024; 16(5): e61449, doi: 10.7759/cureus.61449.
12.
Kara Y.A., Yağız B., Balcı Ö., Karaman A., Özgüner İ.F., Karaman İ. Comparison of open repair and laparoscopic percutaneous internal ring suturing method in repairing inguinal hernia in children. Cureus 2021; 13(4): e14262, doi: 10.7759/cureus.14262.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
The Medical University of Silesia in Katowice, as the Operator of the annales.sum.edu.pl website, processes personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about Users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms, saving cookies in end devices, as well as by collecting web server logs, which are in the possession of the website Operator. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services in accordance with the Privacy policy.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.