Current issue
About the Journal
Scientific Council
Editorial Board
Regulatory and archival policy
Code of publishing ethics
Publisher
Information about the processing of personal data in relation to cookies and newsletter subscription
Archive
For Authors
For Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
Links
Sklep Wydawnictwa SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Privacy policy
Accessibility statement
Reviewers
Annals reviewers in 2025
Annals reviewers in 2024
Annals reviewers in 2023
Annals reviewers in 2022
Annals reviewers in 2021
Annals reviewers in 2020
Annals reviewers in 2019
Annals reviewers in 2018
Annals reviewers in 2017
Annals reviewers in 2016
Annals reviewers in 2015
Annals reviewers in 2014
Annals reviewers in 2013
Annals reviewers in 2012
Class profile and prevalence of overweight and obesity in adolescents – pilot study on the “Health Steps” project
1
Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Human Nutrition, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
2
Zakład Technologii i Oceny Jakości Żywności, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Food Technology and Quality Evaluation, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
3
Zakład Promocji Zdrowia, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Health Promotion, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
4
Zakład Profilaktyki Chorób Sercowo-Naczyniowych, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Cardiovascular Disease Prevention, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Corresponding author
Agnieszka Białek-Dratwa
Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, ul. Jordana 19, 40-808 Zabrze
Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, ul. Jordana 19, 40-808 Zabrze
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2024;1(nr specj.):51-60
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The study aimed to assess the prevalence of overweight and obesity in adolescents aged 11–13 and compare the body weight and body fat content of students in general and sports classes.
Material and methods:
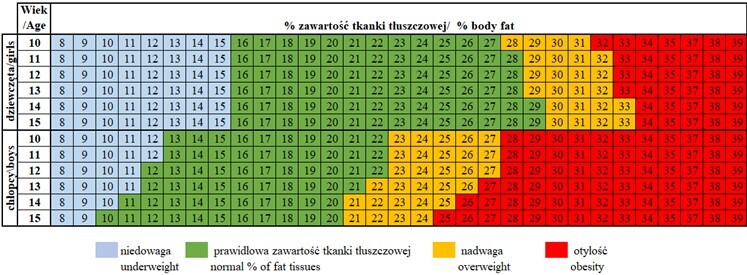
The pilot study involved 352 pupils in grades 6 and 7 from primary schools in Bytom, participating in the project “Health Steps – education and learning as a determinant of a healthy and open society”. The study was meticulously conducted, with careful attention to detail and consideration of the class profile. A sports class, implementing 10 hours of physical education per week, was compared to a general class with 4 hours. To ensure the accuracy of the results, body composition was assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), a widely accepted method. Polish centile grids, a reliable tool, were used to assess body mass index (BMI). Age and gender-specific norms for adolescents were also employed to assess normal body fat, further enhancing the study’s validity.
Results:
In the general profile classes, 77 (25.58%) pupils were overweight, including 36 (22.78%) girls and 41 (28.67%) boys. In sports profile classes, it affected 8 (15.69%) pupils, including 2 (10.53%) girls and 6 (18.75%) boys. In the sports classes, obesity did not occur, while in the general profile classes it affected 13 (4.32%) pupils, including 6 (3.80%) girls and 7 (4.90%) boys. Regarding body fat percentage, 56 (15.91%) students were overweight.
Conclusions:
The study’s key findings reveal that over 25% of adolescents have excessive body weight, with overweight and obesity being less common among pupils in sports classes. Furthermore, over 30% of children have excessive body fat. Notably, girls in sports classes were less likely to be overweight and obese than girls in general profile classes. However, the differences in body fat among boys in the sports and general classes were not statistically significant.
The study aimed to assess the prevalence of overweight and obesity in adolescents aged 11–13 and compare the body weight and body fat content of students in general and sports classes.
Material and methods:
The pilot study involved 352 pupils in grades 6 and 7 from primary schools in Bytom, participating in the project “Health Steps – education and learning as a determinant of a healthy and open society”. The study was meticulously conducted, with careful attention to detail and consideration of the class profile. A sports class, implementing 10 hours of physical education per week, was compared to a general class with 4 hours. To ensure the accuracy of the results, body composition was assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), a widely accepted method. Polish centile grids, a reliable tool, were used to assess body mass index (BMI). Age and gender-specific norms for adolescents were also employed to assess normal body fat, further enhancing the study’s validity.
Results:
In the general profile classes, 77 (25.58%) pupils were overweight, including 36 (22.78%) girls and 41 (28.67%) boys. In sports profile classes, it affected 8 (15.69%) pupils, including 2 (10.53%) girls and 6 (18.75%) boys. In the sports classes, obesity did not occur, while in the general profile classes it affected 13 (4.32%) pupils, including 6 (3.80%) girls and 7 (4.90%) boys. Regarding body fat percentage, 56 (15.91%) students were overweight.
Conclusions:
The study’s key findings reveal that over 25% of adolescents have excessive body weight, with overweight and obesity being less common among pupils in sports classes. Furthermore, over 30% of children have excessive body fat. Notably, girls in sports classes were less likely to be overweight and obese than girls in general profile classes. However, the differences in body fat among boys in the sports and general classes were not statistically significant.
REFERENCES (27)
1.
Obesity and overweight. World Health Organization, 1 March 2024 [online] https://www.who.int/news-room/... [accessed on 8 April 2024].
2.
Kułaga Z., Litwin M., Tkaczyk M., Palczewska I., Zajączkowska M., Zwolińska D. et al. Polish 2010 growth references for school-aged children and adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011; 170(5): 599–609, doi: 10.1007/s00431-010-1329-x.
3.
Mazur A., Zachurzok A., Baran J., Dereń K., Łuszczki E., Weres A. et al. Childhood obesity: position statement of Polish Society of Pediatrics, Polish Society for Pediatric Obesity, Polish Society of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes, the College of Family Physicians in Poland and Polish Association for Study on Obesity. Nutrients 2022; 14(18): 3806, doi: 10.3390/nu14183806.
4.
Xu S., Xue Y. Pediatric obesity: causes, symptoms, prevention and treatment. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016; 11(1): 15–20, doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2853.
5.
Guthold R., Stevens G.A., Riley L.M., Bull F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: a pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1·6 million participants. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020; 4(1): 23–35, doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30323-2.
6.
Owen N., Healy G.N., Matthews C.E., Dunstan D.W. Too much sitting: the population health science of sedentary behavior. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2010; 38(3): 105–113, doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e3181e373a2.
7.
Analizatory składu ciała (Tanita MC-780 P MA BK). Tanita [online] http://www.tanitapolska.pl/ana... profesjonalne-analizatory/tanita-medyczna-waga-i-segmentowy-analizator-skladu-ciala-mc-780p-ma-kolor-czarny.html [accessed on 8 April 2024].
8.
Verney J., Schwartz C., Amiche S., Pereira B., Thivel D. Comparisons of a multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis to the dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan in healthy young adults depending on their physical activity level. J. Hum. Kinet. 2015; 47: 73–80, doi: 10.1515/hukin-2015-0063.
9.
Hills A.P., Andersen L.B., Byrne N.M. Physical activity and obesity in children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011; 45(11): 866–870, doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2011-090199.
10.
Lloyd L.J., Langley-Evans S.C., McMullen S. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk: a systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2010; 34(1): 18–28, doi: 10.1038/ijo.2009.61.
11.
Steene-Johannessen J., Kolle E., Reseland J.E., Anderssen S.A., Andersen L.B. Waist circumference is related to low-grade inflammation in youth. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010; 5(4): 313–319, doi: 10.3109/17477160903497035.
12.
Hills A.P., King N.A., Armstrong T.P. The contribution of physical activity and sedentary behaviours to the growth and development of children and adolescents: implications for overweight and obesity. Sports Med. 2007; 37(6): 533–545, doi: 10.2165/00007256-200737060-00006.
13.
Hills A.P., Okely A.D., Baur L.A. Addressing childhood obesity through increased physical activity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010; 6(10): 543–549, doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.133.
14.
Sallis J.F., Glanz K. Physical activity and food environments: solutions to the obesity epidemic. Milbank Q. 2009; 87(1): 123–154, doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0009.2009.00550.x.
15.
Biddle S.J., Gorely T., Stensel D.J. Health-enhancing physical activity and sedentary behaviour in children and adolescents. J. Sports Sci. 2004; 22(8): 679–701, doi: 10.1080/02640410410001712412.
16.
Global recommendations on physical activity for health. Geneva. World Health Organization 2010.
17.
Calcaterra V., Marin L., Vandoni M., Rossi V., Pirazzi A., Grazi R. et al. Childhood obesity and incorrect body posture: impact on physical activity and the therapeutic role of exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022; 19(24): 16728, doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416728.
18.
Tsiros M.D., Tian E.J., Shultz S.P., Olds T., Hills A.P., Duff J. et al. Obesity, the new childhood disability? An umbrella review on the association between adiposity and physical function. Obes. Rev. 2020; 21(12): e13121, doi: 10.1111/obr.13121.
19.
Cattuzzo M.T., Dos Santos Henrique R., Ré A.H., de Oliveira I.S., Melo B.M., de Sousa Moura M. et al. Motor competence and health related physical fitness in youth: A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016; 19(2): 123–129, doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2014.12.004.
20.
O’Malley G., Keating R., Elmes M., Killeen S., Sheridan N., Murphy S. et al. Standing balance and health-related quality of life in children who are obese. Appetite 2015; 89: 309, doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2014.12.030.
21.
Drenowatz C., Steiner R.P., Brandstetter S., Klenk J., Wabitsch M., Steinacker J.M. Organized sports, overweight, and physical fitness in primary school children in Germany. J. Obes. 2013; 2013: 935245, doi: 10.1155/2013/935245.
22.
Ara I., Vicente-Rodríguez G., Jimenez-Ramirez J., Dorado C., Serrano-Sanchez J.A., Calbet J.A. Regular participation in sports is associated with enhanced physical fitness and lower fat mass in prepubertal boys. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004; 28(12): 1585–1593, doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802754.
23.
Malicevic S., Mirkov D., Milanovic I., Radisavljevic-Janic S., Batez M., Mazic S. Is the physical fitness of schoolchildren dependent on their physical activity levels and nutritional status? The experience from Serbia. Nutr. Hosp. 2022; 39(3): 506–512, doi: 10.20960/nh.03861.
24.
Chaput J.P., Willumsen J., Bull F., Chou R., Ekelund U., Firth J. et al. 2020 WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour for children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: summary of the evidence. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020; 17(1): 141, doi: 10.1186/s12966-020-01037-z.
25.
Suza D.E., Miristia V., Hariati H. Physical activities and incidence of obesity among adolescent in Medan, Indonesia. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2020; 8(E): 198–203, doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2020.4225.
26.
Martin A., Booth J.N., Laird Y., Sproule J., Reilly J.J., Saunders D.H. Physical activity, diet and other behavioural interventions for improving cognition and school achievement in children and adolescents with obesity or overweight. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018; 1: CD009728, doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub3.
27.
Wyszyńska J., Ring-Dimitriou S., Thivel D., Weghuber D., Hadjipanayis A., Grossman Z. et al. Physical activity in the prevention of childhood obesity: the position of the European Childhood Obesity Group and the European Academy of Pediatrics. Front. Pediatr. 2020; 8: 535705, doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.535705.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
The Medical University of Silesia in Katowice, as the Operator of the annales.sum.edu.pl website, processes personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about Users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms, saving cookies in end devices, as well as by collecting web server logs, which are in the possession of the website Operator. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services in accordance with the Privacy policy.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.
You can consent to the processing of data for these purposes, refuse consent or access more detailed information.