Bieżący numer
O czasopiśmie
Rada Naukowa
Kolegium Redakcyjne
Polityka prawno-archiwizacyjna
Kodeks etyki publikacyjnej
Wydawca
Informacja o przetwarzaniu danych osobowych w ramach plików cookies oraz subskrypcji newslettera
Archiwum
Dla autorów
Dla recenzentów
Kontakt
Recenzenci
Recenzenci rocznika 2025
Recenzenci rocznika 2024
Recenzenci rocznika 2023
Recenzenci rocznika 2022
Recenzenci rocznika 2021
Recenzenci rocznika 2020
Recenzenci rocznika 2019
Recenzenci rocznika 2018
Recenzenci rocznika 2017
Recenzenci rocznika 2016
Recenzenci rocznika 2015
Recenzenci rocznika 2014
Recenzenci rocznika 2013
Recenzenci rocznika 2012
Polecamy
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Sklep Wydawnictw SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Polityka prywatności
Deklaracja dostępności
Recenzenci
Recenzenci rocznika 2025
Recenzenci rocznika 2024
Recenzenci rocznika 2023
Recenzenci rocznika 2022
Recenzenci rocznika 2021
Recenzenci rocznika 2020
Recenzenci rocznika 2019
Recenzenci rocznika 2018
Recenzenci rocznika 2017
Recenzenci rocznika 2016
Recenzenci rocznika 2015
Recenzenci rocznika 2014
Recenzenci rocznika 2013
Recenzenci rocznika 2012
Profil klasy a występowanie nadwagi i otyłości w grupie adolescentów – badanie pilotażowe w ramach projektu „Schody Zdrowia”
1
Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Human Nutrition, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
2
Zakład Technologii i Oceny Jakości Żywności, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Food Technology and Quality Evaluation, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
3
Zakład Promocji Zdrowia, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Health Promotion, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
4
Zakład Profilaktyki Chorób Sercowo-Naczyniowych, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach / Department of Cardiovascular Disease Prevention, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Autor do korespondencji
Agnieszka Białek-Dratwa
Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, ul. Jordana 19, 40-808 Zabrze
Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, ul. Jordana 19, 40-808 Zabrze
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2024;1(nr specj.):51-60
SŁOWA KLUCZOWE
DZIEDZINY
STRESZCZENIE
Wstęp:
Celem badania była ocena częstości występowania nadwagi i otyłości u młodzieży w wieku 11–13 lat oraz porównanie masy ciała i zawartości tkanki tłuszczowej uczniów klas o profilu ogólnym i sportowym.
Materiał i metody:
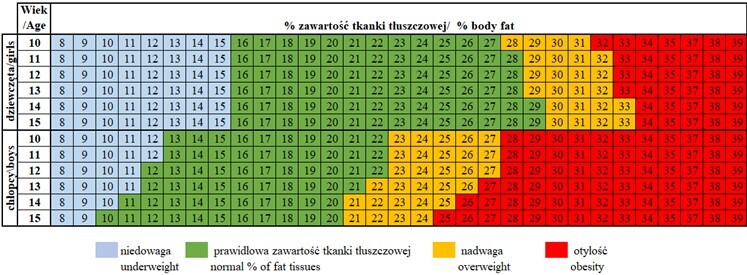
W badaniu pilotażowym uczestniczyło 352 uczniów z klas 6 i 7 szkół podstawowych w Bytomiu, biorących udział w projekcie „Schody Zdrowia – edukacja i nauka wyznacznikiem zdrowego i otwartego społeczeństwa”. W badaniu uwzględniono profil klasy. W klasie sportowej realizowano 10 godzin zajęć z wychowania fizycznego tygodniowo, w klasie ogólnej 4 godziny. Skład ciała oceniano za pomocą analizy impedancji bioelektrycznej (bioelectrical impedance analysis – BIA). Do oceny wskaźnika masy ciała (body mass index – BMI) zastosowano polskie siatki centylowe. Do oceny prawidłowej zawartości tkanki tłuszczowej wykorzystano normy z uwzględnieniem wieku i płci adolescentów.
Wyniki:
W klasach o profilu ogólnym nadwaga występowała u 77 (25,58%) uczniów, w tym u 36 (22,78%) dziewcząt oraz 41 (28,67%) chłopców. W klasach o profilu sportowym dotyczyła 8 (15,69%) uczniów, w tym 2 (10,53%) dziewcząt i 6 (18,75%) chłopców. Otyłość w klasach sportowych nie występowała, a w klasach o profilu ogólnym dotyczyła 13 (4,32%) uczniów, w tym 6 (3,80%) dziewcząt oraz 7 (4,90%) chłopców. Biorąc pod uwagę procentową zawartość tkanki tłuszczowej, nadwaga występowała u 56 (15,91%) uczniów.
Wnioski:
Nadmierna masa ciała dotyczy ponad 25% adolescentów. Nadwaga i otyłość rzadziej występowała u uczniów klas o profilu sportowym. Ponad 30% dzieci ma za dużo tkanki tłuszczowej. Według tego kryterium u dziewcząt w klasach sportowych rzadziej występowała nadwaga i otyłość niż u dziewcząt z klas o profilu ogólnym. Różnice w zawartości tkanki tłuszczowej u chłopców z klasy sportowej i ogólnej były nieistotne statystycznie.
Celem badania była ocena częstości występowania nadwagi i otyłości u młodzieży w wieku 11–13 lat oraz porównanie masy ciała i zawartości tkanki tłuszczowej uczniów klas o profilu ogólnym i sportowym.
Materiał i metody:
W badaniu pilotażowym uczestniczyło 352 uczniów z klas 6 i 7 szkół podstawowych w Bytomiu, biorących udział w projekcie „Schody Zdrowia – edukacja i nauka wyznacznikiem zdrowego i otwartego społeczeństwa”. W badaniu uwzględniono profil klasy. W klasie sportowej realizowano 10 godzin zajęć z wychowania fizycznego tygodniowo, w klasie ogólnej 4 godziny. Skład ciała oceniano za pomocą analizy impedancji bioelektrycznej (bioelectrical impedance analysis – BIA). Do oceny wskaźnika masy ciała (body mass index – BMI) zastosowano polskie siatki centylowe. Do oceny prawidłowej zawartości tkanki tłuszczowej wykorzystano normy z uwzględnieniem wieku i płci adolescentów.
Wyniki:
W klasach o profilu ogólnym nadwaga występowała u 77 (25,58%) uczniów, w tym u 36 (22,78%) dziewcząt oraz 41 (28,67%) chłopców. W klasach o profilu sportowym dotyczyła 8 (15,69%) uczniów, w tym 2 (10,53%) dziewcząt i 6 (18,75%) chłopców. Otyłość w klasach sportowych nie występowała, a w klasach o profilu ogólnym dotyczyła 13 (4,32%) uczniów, w tym 6 (3,80%) dziewcząt oraz 7 (4,90%) chłopców. Biorąc pod uwagę procentową zawartość tkanki tłuszczowej, nadwaga występowała u 56 (15,91%) uczniów.
Wnioski:
Nadmierna masa ciała dotyczy ponad 25% adolescentów. Nadwaga i otyłość rzadziej występowała u uczniów klas o profilu sportowym. Ponad 30% dzieci ma za dużo tkanki tłuszczowej. Według tego kryterium u dziewcząt w klasach sportowych rzadziej występowała nadwaga i otyłość niż u dziewcząt z klas o profilu ogólnym. Różnice w zawartości tkanki tłuszczowej u chłopców z klasy sportowej i ogólnej były nieistotne statystycznie.
FINANSOWANIE
Praca realizowana w ramach programu „Społecznej Odpowiedzialności Nauki”, finansowanym ze środków Ministerstwa Edukacji i Nauki.
KONFLIKT INTERESÓW
Nie zadeklarowano.
REFERENCJE (27)
1.
Obesity and overweight. World Health Organization, 1 March 2024 [online] https://www.who.int/news-room/... [accessed on 8 April 2024].
2.
Kułaga Z., Litwin M., Tkaczyk M., Palczewska I., Zajączkowska M., Zwolińska D. et al. Polish 2010 growth references for school-aged children and adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011; 170(5): 599–609, doi: 10.1007/s00431-010-1329-x.
3.
Mazur A., Zachurzok A., Baran J., Dereń K., Łuszczki E., Weres A. et al. Childhood obesity: position statement of Polish Society of Pediatrics, Polish Society for Pediatric Obesity, Polish Society of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes, the College of Family Physicians in Poland and Polish Association for Study on Obesity. Nutrients 2022; 14(18): 3806, doi: 10.3390/nu14183806.
4.
Xu S., Xue Y. Pediatric obesity: causes, symptoms, prevention and treatment. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016; 11(1): 15–20, doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2853.
5.
Guthold R., Stevens G.A., Riley L.M., Bull F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: a pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1·6 million participants. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020; 4(1): 23–35, doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30323-2.
6.
Owen N., Healy G.N., Matthews C.E., Dunstan D.W. Too much sitting: the population health science of sedentary behavior. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2010; 38(3): 105–113, doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e3181e373a2.
7.
Analizatory składu ciała (Tanita MC-780 P MA BK). Tanita [online] http://www.tanitapolska.pl/ana... profesjonalne-analizatory/tanita-medyczna-waga-i-segmentowy-analizator-skladu-ciala-mc-780p-ma-kolor-czarny.html [accessed on 8 April 2024].
8.
Verney J., Schwartz C., Amiche S., Pereira B., Thivel D. Comparisons of a multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis to the dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan in healthy young adults depending on their physical activity level. J. Hum. Kinet. 2015; 47: 73–80, doi: 10.1515/hukin-2015-0063.
9.
Hills A.P., Andersen L.B., Byrne N.M. Physical activity and obesity in children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011; 45(11): 866–870, doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2011-090199.
10.
Lloyd L.J., Langley-Evans S.C., McMullen S. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk: a systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2010; 34(1): 18–28, doi: 10.1038/ijo.2009.61.
11.
Steene-Johannessen J., Kolle E., Reseland J.E., Anderssen S.A., Andersen L.B. Waist circumference is related to low-grade inflammation in youth. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010; 5(4): 313–319, doi: 10.3109/17477160903497035.
12.
Hills A.P., King N.A., Armstrong T.P. The contribution of physical activity and sedentary behaviours to the growth and development of children and adolescents: implications for overweight and obesity. Sports Med. 2007; 37(6): 533–545, doi: 10.2165/00007256-200737060-00006.
13.
Hills A.P., Okely A.D., Baur L.A. Addressing childhood obesity through increased physical activity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010; 6(10): 543–549, doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.133.
14.
Sallis J.F., Glanz K. Physical activity and food environments: solutions to the obesity epidemic. Milbank Q. 2009; 87(1): 123–154, doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0009.2009.00550.x.
15.
Biddle S.J., Gorely T., Stensel D.J. Health-enhancing physical activity and sedentary behaviour in children and adolescents. J. Sports Sci. 2004; 22(8): 679–701, doi: 10.1080/02640410410001712412.
16.
Global recommendations on physical activity for health. Geneva. World Health Organization 2010.
17.
Calcaterra V., Marin L., Vandoni M., Rossi V., Pirazzi A., Grazi R. et al. Childhood obesity and incorrect body posture: impact on physical activity and the therapeutic role of exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022; 19(24): 16728, doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416728.
18.
Tsiros M.D., Tian E.J., Shultz S.P., Olds T., Hills A.P., Duff J. et al. Obesity, the new childhood disability? An umbrella review on the association between adiposity and physical function. Obes. Rev. 2020; 21(12): e13121, doi: 10.1111/obr.13121.
19.
Cattuzzo M.T., Dos Santos Henrique R., Ré A.H., de Oliveira I.S., Melo B.M., de Sousa Moura M. et al. Motor competence and health related physical fitness in youth: A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016; 19(2): 123–129, doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2014.12.004.
20.
O’Malley G., Keating R., Elmes M., Killeen S., Sheridan N., Murphy S. et al. Standing balance and health-related quality of life in children who are obese. Appetite 2015; 89: 309, doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2014.12.030.
21.
Drenowatz C., Steiner R.P., Brandstetter S., Klenk J., Wabitsch M., Steinacker J.M. Organized sports, overweight, and physical fitness in primary school children in Germany. J. Obes. 2013; 2013: 935245, doi: 10.1155/2013/935245.
22.
Ara I., Vicente-Rodríguez G., Jimenez-Ramirez J., Dorado C., Serrano-Sanchez J.A., Calbet J.A. Regular participation in sports is associated with enhanced physical fitness and lower fat mass in prepubertal boys. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004; 28(12): 1585–1593, doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802754.
23.
Malicevic S., Mirkov D., Milanovic I., Radisavljevic-Janic S., Batez M., Mazic S. Is the physical fitness of schoolchildren dependent on their physical activity levels and nutritional status? The experience from Serbia. Nutr. Hosp. 2022; 39(3): 506–512, doi: 10.20960/nh.03861.
24.
Chaput J.P., Willumsen J., Bull F., Chou R., Ekelund U., Firth J. et al. 2020 WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour for children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: summary of the evidence. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020; 17(1): 141, doi: 10.1186/s12966-020-01037-z.
25.
Suza D.E., Miristia V., Hariati H. Physical activities and incidence of obesity among adolescent in Medan, Indonesia. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2020; 8(E): 198–203, doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2020.4225.
26.
Martin A., Booth J.N., Laird Y., Sproule J., Reilly J.J., Saunders D.H. Physical activity, diet and other behavioural interventions for improving cognition and school achievement in children and adolescents with obesity or overweight. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018; 1: CD009728, doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub3.
27.
Wyszyńska J., Ring-Dimitriou S., Thivel D., Weghuber D., Hadjipanayis A., Grossman Z. et al. Physical activity in the prevention of childhood obesity: the position of the European Childhood Obesity Group and the European Academy of Pediatrics. Front. Pediatr. 2020; 8: 535705, doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.535705.
Udostępnij
ARTYKUŁ POWIĄZANY
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, jako Operator Serwisu annales.sum.edu.pl, przetwarza dane osobowe zbierane podczas odwiedzania Serwisu. Realizacja funkcji pozyskiwania informacji o Użytkownikach i ich zachowaniu odbywa się poprzez dobrowolnie wprowadzone w formularzach informacje, zapisywanie w urządzeniach końcowych plików cookies (tzw. ciasteczka), a także poprzez gromadzenie logów serwera www, będącego w posiadaniu Operatora Serwisu. Dane, w tym pliki cookies, wykorzystywane są w celu realizacji usług zgodnie z Polityką prywatności.
Możesz wyrazić zgodę na przetwarzanie danych w tych celach, odmówić zgody lub uzyskać dostęp do bardziej szczegółowych informacji.
Możesz wyrazić zgodę na przetwarzanie danych w tych celach, odmówić zgody lub uzyskać dostęp do bardziej szczegółowych informacji.