Bieżący numer
O czasopiśmie
Rada Naukowa
Kolegium Redakcyjne
Polityka prawno-archiwizacyjna
Kodeks etyki publikacyjnej
Wydawca
Informacja o przetwarzaniu danych osobowych w ramach plików cookies oraz subskrypcji newslettera
Archiwum
Dla autorów
Dla recenzentów
Kontakt
Recenzenci
Recenzenci rocznika 2025
Recenzenci rocznika 2024
Recenzenci rocznika 2023
Recenzenci rocznika 2022
Recenzenci rocznika 2021
Recenzenci rocznika 2020
Recenzenci rocznika 2019
Recenzenci rocznika 2018
Recenzenci rocznika 2017
Recenzenci rocznika 2016
Recenzenci rocznika 2015
Recenzenci rocznika 2014
Recenzenci rocznika 2013
Recenzenci rocznika 2012
Polecamy
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Sklep Wydawnictw SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Polityka prywatności
Deklaracja dostępności
Recenzenci
Recenzenci rocznika 2025
Recenzenci rocznika 2024
Recenzenci rocznika 2023
Recenzenci rocznika 2022
Recenzenci rocznika 2021
Recenzenci rocznika 2020
Recenzenci rocznika 2019
Recenzenci rocznika 2018
Recenzenci rocznika 2017
Recenzenci rocznika 2016
Recenzenci rocznika 2015
Recenzenci rocznika 2014
Recenzenci rocznika 2013
Recenzenci rocznika 2012
Prebiotyki – fundament profilaktyki zdrowotnej
1
Students’ Scientific Club, Department of Human Nutrition, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom,
Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
2
Department of Human Nutrition, Faculty of Public Health in Bytom, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Autor do korespondencji
Wiktoria Ficoń
Studenckie Koło Naukowe, Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu ŚUM, ul. Jordana 19, 41-808 Zabrze
Studenckie Koło Naukowe, Zakład Żywienia Człowieka, Wydział Zdrowia Publicznego w Bytomiu ŚUM, ul. Jordana 19, 41-808 Zabrze
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2025;1(nr specj.):31-39
SŁOWA KLUCZOWE
DZIEDZINY
STRESZCZENIE
Wprowadzenie:
Prebiotyki to substancje, które wspierają rozwój i aktywność mikrobioty jelitowej poprzez stymulację wzrostu i funkcjonowania bakterii zasiedlających jelito grube. Składniki te nie ulegają trawieniu w przewodzie pokarmowym człowieka. Należą do nich m.in. skrobia i błonnik pokarmowy.
Materiał i metody:
Materiał badawczy stanowiła grupa 140 osób – 99 kobiet i 41 mężczyzn w wieku od 30 do 50 lat. Metodą badawczą zastosowaną w analizie była ankieta diagnostyczna, a techniką badawczą autorski kwestionariusz.
Wyniki:
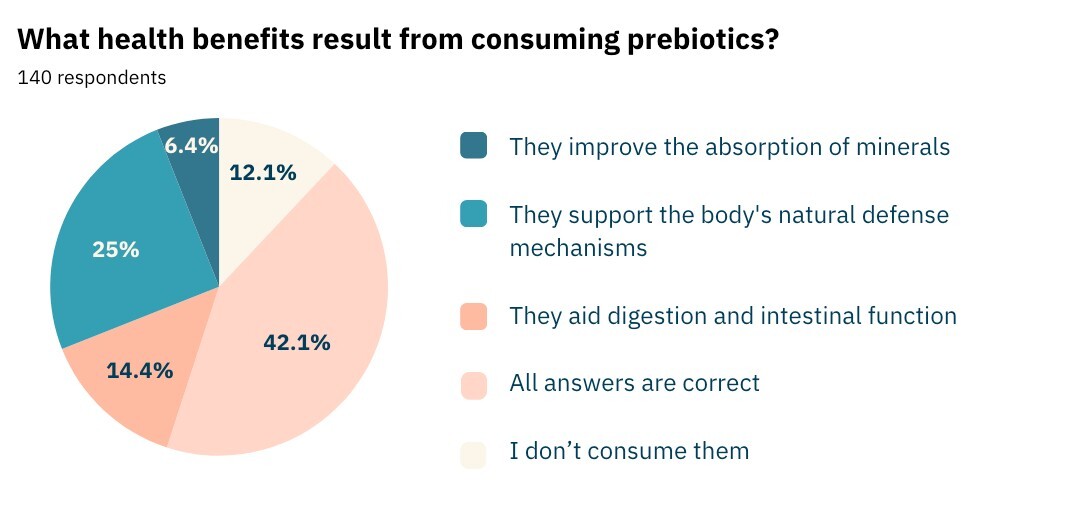
Poprawną definicję terminu „prebiotyk” wybrało 57,1% uczestników, podczas gdy 25% pomyliło go z pro-biotykiem. Określenia „probiotyk” i „prebiotyk” uznało za synonimiczne 20% respondentów, natomiast 12,1% nie potrafiło udzielić odpowiedzi na to pytanie. Ponad połowa uczestników badania (57,6%) wie, że probiotyki można łączyć z prebiotykami, ale jedynie 48,6% potrafi wskazać produkty, które je zawierają. Według 65% badanych prebiotyki ulegają fermentacji w przewodzie pokarmowym, co stanowi poprawną odpowiedź, podczas gdy 35% udzieliło błędnej odpowiedzi.
Wnioski:
Niektórzy respondenci są świadomi pozytywnego wpływu prebiotyków na zdrowie jelit. Jednak dla wielu z nich konkretne korzyści zdrowotne oraz produkty bogate w prebiotyki pozostają niejasne. Wyniki wskazują na potrzebę dalszej edukacji społeczeństwa, w tym szczegółowego wyjaśnienia różnic między prebiotykami a probiotykami oraz ich roli w żywieniu człowieka.
Prebiotyki to substancje, które wspierają rozwój i aktywność mikrobioty jelitowej poprzez stymulację wzrostu i funkcjonowania bakterii zasiedlających jelito grube. Składniki te nie ulegają trawieniu w przewodzie pokarmowym człowieka. Należą do nich m.in. skrobia i błonnik pokarmowy.
Materiał i metody:
Materiał badawczy stanowiła grupa 140 osób – 99 kobiet i 41 mężczyzn w wieku od 30 do 50 lat. Metodą badawczą zastosowaną w analizie była ankieta diagnostyczna, a techniką badawczą autorski kwestionariusz.
Wyniki:
Poprawną definicję terminu „prebiotyk” wybrało 57,1% uczestników, podczas gdy 25% pomyliło go z pro-biotykiem. Określenia „probiotyk” i „prebiotyk” uznało za synonimiczne 20% respondentów, natomiast 12,1% nie potrafiło udzielić odpowiedzi na to pytanie. Ponad połowa uczestników badania (57,6%) wie, że probiotyki można łączyć z prebiotykami, ale jedynie 48,6% potrafi wskazać produkty, które je zawierają. Według 65% badanych prebiotyki ulegają fermentacji w przewodzie pokarmowym, co stanowi poprawną odpowiedź, podczas gdy 35% udzieliło błędnej odpowiedzi.
Wnioski:
Niektórzy respondenci są świadomi pozytywnego wpływu prebiotyków na zdrowie jelit. Jednak dla wielu z nich konkretne korzyści zdrowotne oraz produkty bogate w prebiotyki pozostają niejasne. Wyniki wskazują na potrzebę dalszej edukacji społeczeństwa, w tym szczegółowego wyjaśnienia różnic między prebiotykami a probiotykami oraz ich roli w żywieniu człowieka.
REFERENCJE (24)
1.
Eid N.M., Alsolami G.A., Al-Nuafie H.D., Malibari H.W., Alsolami W.D., Enani S. Assessment of Knowledge, Perception, and Practices Regarding Probiotics and Prebiotics Among Clinicians in Saudi Arabia: A Pilot Study. Cureus. 2024; 16(1): e52080, doi: 10.7759/cureus.52080.
2.
Gibson G.R., Hutkins R., Sanders M.E., Prescott S.L., Reimer R.A., Salminen S.J. et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 14(8): 491–502, doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75.
3.
You S., Ma Y., Yan B., Pei W., Wu Q., Ding C., Huang C. The promotion mechanism of prebiotics for probiotics: A review. Front Nutr. 2022; 9: 1000517, doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1000517.
4.
Kumari A., Rashmi K.G., Sudhakaran A.V., Warrier A.S., Singh N.K. Unveiling the Health Benefits of Prebiotics: A Comprehensive Review. Indian J Microbiol. 2024: 64(2): 376–388, doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01235-4.
5.
Markowiak-Kopeć P., Śliżewska K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients. 2020; 12(4): 1107, doi: 10.3390/nu12041107.
6.
Quigley E.M.M. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Digestive Health. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 17(2): 333–344, doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.028.
7.
Obayomi O.V., Olaniran A.F., Owa S.O. Unveiling the role of functional foods with emphasis on prebiotics and probiotics in human health: A review. JFF. 2024; 119: 106337, doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106337.
8.
Gul S., Durante-Mangoni E. Unraveling the Puzzle: Health Benefits of Probiotics–A Comprehensive Review. J Clin Med. 2024; 13(5): 1436, doi: 10.3390/jcm13051436.
9.
Alqaydi T.K., Bedir A.S., Abu-Elsaoud A.M., El-Tarabily K.A., Al Raish S.M. An Assessment of the Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Probiotics and Prebiotics among the Population of the United Arab Emirates. Foods. 2024; 13(14): 2219, doi: 10.3390/foods13142219.
10.
Davani-Davari D., Negahdaripour M., Karimzadeh I., Seifan M., Mohkam M., Masoumi S.J. et al. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods. 2019; 8(3): 92, doi: 10.3390/foods8030092.
11.
Cho S.Y., Kim J., Lee J.H., Sim J.H., Cho D.H., Bae I.H. et al. Modulation of gut microbiota and delayed immunosenescence as a result of syringaresinol consumption in middle-aged mice. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 39026, doi: 10.1038/srep39026.
12.
Bevilacqua A., Campaniello D., Speranza B., Racioppo A., Sinigaglia M., Corbo M.R. An Update on Prebiotics and on Their Health Effects. Foods. 2024; 13(3): 446, doi: 10.3390/foods13030446.
13.
Cerdó T., García-Santos J.A., G Bermúdez M.G., Campoy C. The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3): 635, doi: 10.3390/nu11030635.
14.
Hassan N.E., El-Masry S.A., El Shebini S.M., Ahmed N.H., Mehanna N.S., Abdel Wahed M.M., et al. Effect of weight loss program using prebiotics and probiotics on body composition, physique, and metabolic products: longitudinal intervention study. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1): 10960, doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61130-2.
15.
Petrut S.M., Bragaru A.M., Munteanu A.E., Moldovan A.D., Moldovan C.A., Rusu E. Gut over Mind: Exploring the Powerful Gut–Brain Axis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(5): 842, doi: 10.3390/nu17050842.
16.
Ansari F., Neshat M., Pourjafar H., Jafari S.M., Samakkhah S.A., Mirzakhani E. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in modulating of the gut-brain axis. Front Nutr. 2023; 10: 1173660, doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1173660.
17.
Bistas K.G., Tabet J.P. The Benefits of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Mental Health. Cureus. 2023; 15(8): e43217, doi: 10.7759/cureus.43217.
18.
Dalile B., Boyle N.B., Ruiz F.T., Chakrabarti A., Respondek F., Dodd G.F. et al. Targeting Cognitive Resilience through Prebiotics: A Focused Perspective. Adv Nutr. 2025; 16(1): 100343, doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2024.100343.
19.
Deehan E.C., Antwan S.A., Witwer R.S., Guerra P., John T., Monheit L. Revisiting the Concepts of Prebiotic and Prebiotic Effect in Light of Scientific and Regulatory Progress–A Consensus Paper From the Global Prebiotic Association. Adv Nutr. 2024; 15(12): 100329, doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2024.100329.
20.
Nawal A.A. Saudi Arabian Women’s Knowledge of Probiotics and Prebiotics. Progress in Nutrition. 2021; 23(4): e2021154, doi: 10.23751/pn.v23i4.11503.
21.
Khalesi S., Vandelanotte C., Thwaite T., Russell A.M.T., Dawson D., Williams S.L. Awareness and Attitudes of Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics in Australian Adults. J Diet Suppl. 2021; 18(4): 418–432, doi: 10.1080/19390211.2020.1783420.
22.
Precup G., Pocol C.B., Teleky B.E., Vodnar D.C. Awareness, Knowledge, and Interest about Prebiotics–A Study among Romanian Consumers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19(3): 1208, doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031208.
23.
Patait M.R., Saraf K.V., Wakchaure P.M. Assessment of Knowledge and Awareness of Probiotics Among the Dental Post-graduate Students – A Questionnaire Study. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2022; 34: 68–75, doi: 10.4103/jiaomr.jiaomr_231_21.
24.
Fermin D., Alshammari S., Morgadinho J., Halverson T., Anwar S., Senthilselvan A. et al. Investigating the Knowledge of Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Synbiotics That May Help to Improve the Gut-Organ Axis Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Cureus. 2024; 16(8): e66994, doi: 10.7759/cureus.66994.
Udostępnij
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, jako Operator Serwisu annales.sum.edu.pl, przetwarza dane osobowe zbierane podczas odwiedzania Serwisu. Realizacja funkcji pozyskiwania informacji o Użytkownikach i ich zachowaniu odbywa się poprzez dobrowolnie wprowadzone w formularzach informacje, zapisywanie w urządzeniach końcowych plików cookies (tzw. ciasteczka), a także poprzez gromadzenie logów serwera www, będącego w posiadaniu Operatora Serwisu. Dane, w tym pliki cookies, wykorzystywane są w celu realizacji usług zgodnie z Polityką prywatności.
Możesz wyrazić zgodę na przetwarzanie danych w tych celach, odmówić zgody lub uzyskać dostęp do bardziej szczegółowych informacji.
Możesz wyrazić zgodę na przetwarzanie danych w tych celach, odmówić zgody lub uzyskać dostęp do bardziej szczegółowych informacji.