Bieżący numer
O czasopiśmie
Rada Naukowa
Kolegium Redakcyjne
Polityka prawno-archiwizacyjna
Kodeks etyki publikacyjnej
Wydawca
Informacja o przetwarzaniu danych osobowych w ramach plików cookies oraz subskrypcji newslettera
Archiwum
Dla autorów
Dla recenzentów
Kontakt
Recenzenci
Recenzenci rocznika 2025
Recenzenci rocznika 2024
Recenzenci rocznika 2023
Recenzenci rocznika 2022
Recenzenci rocznika 2021
Recenzenci rocznika 2020
Recenzenci rocznika 2019
Recenzenci rocznika 2018
Recenzenci rocznika 2017
Recenzenci rocznika 2016
Recenzenci rocznika 2015
Recenzenci rocznika 2014
Recenzenci rocznika 2013
Recenzenci rocznika 2012
Polecamy
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
Sklep Wydawnictw SUM
Biblioteka Główna SUM
Polityka prywatności
Deklaracja dostępności
Recenzenci
Recenzenci rocznika 2025
Recenzenci rocznika 2024
Recenzenci rocznika 2023
Recenzenci rocznika 2022
Recenzenci rocznika 2021
Recenzenci rocznika 2020
Recenzenci rocznika 2019
Recenzenci rocznika 2018
Recenzenci rocznika 2017
Recenzenci rocznika 2016
Recenzenci rocznika 2015
Recenzenci rocznika 2014
Recenzenci rocznika 2013
Recenzenci rocznika 2012
Lymphomatoid papulosis w populacji pediatrycznej – opis przypadku i rozważania terapeutyczne
1
Department of Dermatology and Vascular Anomalies, Center of Pediatrics John Paul II, Sosnowiec
Zaznaczeni autorzy mieli równy wkład w przygotowanie tego artykułu
Autor do korespondencji
Michał Dec
Oddział Dermatologii i Leczenia Anomalii Naczyniowych dla Dzieci, Centrum Pediatrii im. Jana Pawła II w Sosnowcu Sp. z o.o., ul. G. Zapolskiej 3, 41-218 Sosnowiec
Oddział Dermatologii i Leczenia Anomalii Naczyniowych dla Dzieci, Centrum Pediatrii im. Jana Pawła II w Sosnowcu Sp. z o.o., ul. G. Zapolskiej 3, 41-218 Sosnowiec
Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2024;78:24-30
SŁOWA KLUCZOWE
lymphomatoid papulosischoroby limfoproliferacyjne z komórek CD30+fototerapiaimmunohistochemiametotreksat
DZIEDZINY
STRESZCZENIE
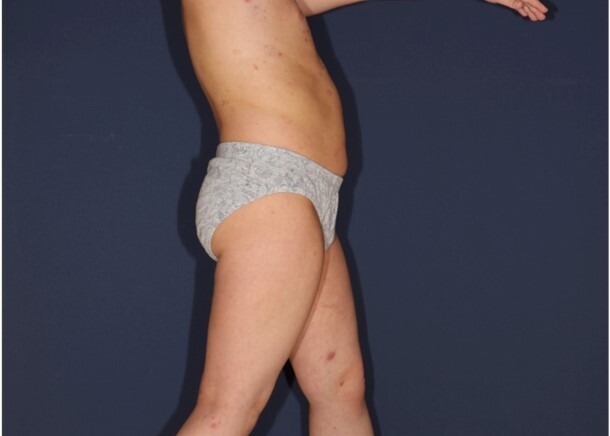
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) jest rzadką chorobą skóry, najczęściej obserwowaną u dorosłych, a jej występowanie
w populacji pediatrycznej jest niezwykle rzadkie. W pracy przedstawiono przypadek 6-letniego dziecka płci męskiej,
u którego stwierdzono cechy kliniczne i histopatologiczne zgodne z rozpoznaniem LyP. Na skórze pacjenta obserwowano liczne rumieniowe grudki zlokalizowane na tułowiu i kończynach, a towarzyszył im łagodny świąd. Zmiany chorobowe pojawiały się nawrotowo, następnie ustępowały i zmieniały morfologię. W badaniu przedmiotowym nie stwierdzono limfadenopatii ani objawów ogólnoustrojowych. W badaniu histopatologicznym w skórze właściwej stwierdzono gęsty naciek limfocytów atypowych z hiperchromatycznymi i nieregularnymi jądrami komórkowymi. Analiza immunohistochemiczna potwierdziła ekspresję CD30 w naciekających komórkach, co potwierdza rozpoznanie LyP.
W celu złagodzenia świądu i stanu zapalnego podawano miejscowo glikokortykosteroidy, chociaż uzyskano jedynie minimalne złagodzenie objawów. Korzystne efekty fototerapii wąskopasmowej UVB 311 obserwowano przez cztery miesiące. Niemniej jednak po zaprzestaniu leczenia zaobserwowano ponowne pojawienie się zarówno zmian guzkowych, jak i mniejszych zmian grudkowych. W związku z tym rozpoczęto schemat terapeutyczny polegający na podawaniu metotreksatu w dawce 10 mg raz na tydzień.
Leczenie LyP różni się zależnie od ciężkości zmian i objawów u pacjenta. Decyzje dotyczące leczenia należy dokładnie rozważyć ze względu na stosunkowo łagodny charakter choroby.
Rozpoznanie LyP u dzieci i młodzieży stanowi wyzwanie ze względu na rzadkość występowania choroby i możliwość błędnego rozpoznania tej jednostki chorobowej z chłoniakami złośliwymi. Histopatologia i immunohistochemia odgrywają kluczową rolę w odróżnianiu LyP od bardziej agresywnych jednostek chorobowych.
REFERENCJE (48)
1.
Wang L., Chen F., Zhao S., Wang X., Fang J., Zhu X. Lymphomatoid papulosis subtype C: A case report and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021; 34(1): e14452, doi: 10.1111/dth.14452.
2.
Bekkenk M.W., Geelen F.A., van Voorst Vader P.C., Heule F., Geerts M.L., van Vloten W.A. et al. Primary and secondary cutaneous CD30(+) lymphoproliferative disorders: a report from the Dutch Cutaneous Lymphoma Group on the long-term follow-up data of 219 patients and guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 2000; 95(12): 3653–3661.
3.
Wieser I., Oh C.W., Talpur R., Duvic M. Lymphomatoid papulosis: Treatment response and associated lymphomas in a study of 180 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016; 74(1): 59–67, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.09.013.
4.
Miquel J., Fraitag S., Hamel-Teillac D., Molina T., Brousse N., de Prost Y. et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis in children: a series of 25 cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014; 171(5): 1138–1146, doi: 10.1111/bjd.13061.
5.
Burg G., Kempf W., Haeffner A., Döbbeling U., Nestle F.O., Böni R. et al. From inflammation to neoplasia: new concepts in the pathogenesis of cutaneous lymphomas. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2002; 160: 271–280, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59410-6_32.
6.
Nowicka D., Mertowska P., Mertowski S., Hymos A., Forma A., Michalski A. et al. Etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for lymphomatoid papulosis with particular emphasis on the role of the immune system. Cells 2022; 11(22): 3697, doi: 10.3390/cells11223697.
7.
Namba H., Hamada T., Iwatsuki K. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-positive lymphomatoid papulosis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2016; 26(2): 194–195, doi: 10.1684/ejd.2015.2707.
8.
Kempf W., Kadin M.E., Dvorak A.M., Lord C.C., Burg G., Letvin N.L. et al. Endogenous retroviral elements, but not exogenous retroviruses, are detected in CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders of the skin. Carcinogenesis 2003; 24(2): 301–306, doi: 10.1093/carcin/24.2.301.
9.
Kempf W., Kadin M.E., Kutzner H., Lord C.L., Burg G., Letvin N.L. et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis and human herpesviruses – A PCR-based evaluation for the presence of human herpesvirus 6, 7 and 8 related herpesviruses. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2001; 28(1): 29–33, doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0560.2001.280103.x.
10.
Hooper M.J., Lee W.J., LeWitt T.M., Nguyen C., Griffin T., Chung C. et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomatoid papules: A sign of immunosuppression resembling lymphomatoid papulosis. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2023; 45(12): 789–800, doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000002479.
11.
Kim Y.C., Yang W.I., Lee M.G., Kim S.N., Cho K.H., Lee S.J. et al. Epstein-Barr virus in CD30 anaplastic large cell lymphoma involving the skin and lymphomatoid papulosis in South Korea. Int. J. Dermatol. 2006; 45(11): 1312–1316, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02951.x.
12.
Zhao P., Gish T.J., Mannschreck D., Marchi E., Cropley T.G. Zosteriform mycosis fungoides and lymphomatoid papulosis arising in an area of prior herpes zoster. JAAD Case Rep. 2023; 40: 84–88, doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2023.08.018.
13.
Schiemann W.P., Pfeifer W.M., Levi E., Kadin M.E., Lodish H.F. A deletion in the gene for transforming growth factor beta type I receptor abolishes growth regulation by transforming growth factor beta in a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 1999; 94(8): 2854–2861.
14.
Haro R., Juarez A., Díaz J.L., Santonja C., Manzarbeitia F., Requena L. Regional lymphomatoid papulosis of the breast restricted to an area of prior radiotherapy. Cutis. 2016; 97(5): E15–19.
15.
Samaraweera A.P.R., Cohen S.N., Akay E.M., Evangelou N. Lymphomatoid papulosis: A cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorder in a patient on fingolimod for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2016; 22(1): 122–124, doi: 10.1177/1352458515597568.
16.
Park J.H., Lee J., Lee J.H., Lee D.Y., Koh E.M. Lymphomatoid papulosis in a patient treated with adalimumab for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Dermatology 2012; 225(3): 259–263, doi: 10.1159/000345104.
17.
Matoula T., Nikolaou V., Marinos L., Katsavos S., Nasis G., Economidi A. et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis type D in a fingolimod-treated multiple sclerosis patient. Mult. Scler. 2016; 22(12): 1630–1631, doi: 10.1177/1352458516642032.
18.
Shirani A., Dalton S.R., Avery E.J., Arcot Jayagopal L., Meyer C., Stuve O. et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis in a patient treated with glatiramer acetate and the glatiramoid Glatopa for multiple sclerosis: A case report. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2021; 13: 11795735211053784, doi: 10.1177/11795735211053784.
19.
Outlaw W., Fleischer A., Bloomfeld R. Lymphomatoid papulosis in a patient with Crohnʼs disease treated with infliximab. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009; 15(7): 965–966, doi: 10.1002/ibd.20762.
20.
Leo A.M., Ermolovich T. Lymphomatoid papulosis while on efalizumab. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009; 61(3): 540–541, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.12.010.
21.
Stoll J.R., Willner J., Oh Y., Pulitzer M., Moskowitz A., Horwitz S. et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Part I: Clinical and histologic features and diagnosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021; 85(5): 1073–1090, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.04.080.
22.
Korpusik D., Ruzicka T. Klinische Verlaufsformen und Therapie der lymphomatoiden Papulose. Hautarzt 2007; 58(10): 870–881.
23.
Moy A., Sun J., Ma S., Seminario-Vidal L. Lymphomatoid papulosis and other lymphoma-like diseases. Dermatol. Clin. 2019; 37(4): 471–482, doi: 10.1016/j.det.2019.05.005.
24.
Pomsoong C., Suchonwanit P., Chanprapaph K., Rattanakaemakorn P., Rutnin S. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta and lymphomatoid papulosis type F: A case report of two entities in one patient. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022; 15: 1759–1765, doi: 10.2147/CCID.S379577.
25.
Fujimura T., Lyu C., Tsuchiyama K., Aiba S. CD30-positive angioinvasive lymphomatoid papulosis (type E) developing from parapsoriasis en plaque. Case Rep. Oncol. 2018; 11(3): 850–854, doi: 10.1159/000495689.
26.
Heald P., Subtil A., Breneman D., Wilson L.D. Persistent agmination of lymphomatoid papulosis: an equivalent of limited plaque mycosis fungoides type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007; 57(6): 1005–1011, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.05.046.
27.
Steinhoff M., Assaf C., Sterry W. Persistent agmination of lymphomatoid papulosis: not a new entity, but localized lymphomatoid papulosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008; 59(1): 164–165; author reply 165, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.12.039.
28.
Martinez-Cabriales S.A., Walsh S., Sade S., Shear N.H. Lymphomatoid papulosis: an update and review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020; 34(1): 59–73, doi: 10.1111/jdv.15931.
29.
Swerdlow S.H., Campo E., Pileri S.A., Harris N.L., Stein H., Siebert R. et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016; 127(20): 2375–2390, doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569.
30.
Kempf W., Kazakov D.V., Schärer L., Rütten A., Mentzel T., Paredes B.E. et al. Angioinvasive lymphomatoid papulosis: a new variant simulating aggressive lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013; 37(1): 1–13, doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182648596.
31.
Saggini A., Gulia A., Argenyi Z., Fink-Puches R., Lissia A., Magaña M. et al. A variant of lymphomatoid papulosis simulating primary cutaneous aggressive epidermotropic CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma. Description of 9 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010; 34(8): 1168–1175, doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181e75356.
32.
Ross N.A., Truong H., Keller M.S., Mulholland J.K., Lee J.B., Sahu J. Follicular lymphomatoid papulosis: An eosinophilic-rich follicular subtype masquerading as folliculitis clinically and histologically. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2016; 38(1): e1–10, doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000395.
33.
Gheucă Solovăstru L., Vâţă D., Ciobanu D., Stătescu L., Rotaru M. The importance of histopathology findings in lymphomatoid papulosis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014; 55(4): 1527–1530.
34.
Werner B., Massone C., Kerl H., Cerroni L. Large CD30-positive cells in benign, atypical lymphoid infiltrates of the skin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2008; 35(12): 1100–1107, doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2007.00979.x.
35.
Abdulla F.R., Zhang W., Wu X., Honda K., Qin H., Cho H. et al. Genomic analysis of cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. JID Innov. 2021; 2(1): 100068, doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100068.
36.
Nikolaenko L., Zain J., Rosen S.T., Querfeld C. CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. Cancer Treat. Res. 2019; 176: 249–268, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-99716-2_12.
37.
Kempf W., Mitteldorf C., Karai L.J., Robson A. Lymphomatoid papulosis – making sense of the alphabet soup: a proposal to simplify terminology. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2017; 15(4): 390–394, doi: 10.1111/ddg.13207.
38.
Prieto-Torres L., Rodriguez-Pinilla S.M., Onaindia A., Ara M., Requena L., Piris M.Á. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica 2019; 104(2): 226–235, doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.197152.
39.
Nijsten T., Curiel-Lewandrowski C., Kadin M.E. Lymphomatoid papulosis in children: a retrospective cohort study of 35 cases. Arch. Dermatol. 2004; 140(3): 306–312, doi: 10.1001/archderm.140.3.306.
40.
de Souza A., Camilleri M.J., Wada D.A., Appert D.L., Gibson L.E., el-Azhary R.A. Clinical, histopathologic, and immunophenotypic features of lymphomatoid papulosis with CD8 predominance in 14 pediatric patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009; 61(6): 993–1000, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2009.05.014.
41.
Kempf W. CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders: histopathology, differential diagnosis, new variants, and simulators. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2006; 33 Suppl 1: 58–70, doi: 10.1111/j.0303-6987.2006.00548.x.
42.
Thomsen K., Wantzin G.L. Lymphomatoid papulosis. A follow-up study of 30 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987; 17(4): 632–636, doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70248-5.
43.
Everett M.A. Treatment of lymphomatoid papulosis with methotrexate. Br. J. Dermatol. 1984; 111(5): 631, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb06640.x.
44.
Vonderheid E.C., Sajjadian A., Kadin M.E. Methotrexate is effective therapy for lymphomatoid papulosis and other primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996; 34(3): 470–481, doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90442-9.
45.
Bruijn M.S., Horváth B., van Voorst Vader P.C., Willemze R., Vermeer M.H. Recommendations for treatment of lymphomatoid papulosis with methotrexate: a report from the Dutch Cutaneous Lymphoma Group. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015; 173(5): 1319–1322, doi: 10.1111/bjd.13920.
46.
Newland K.M., McCormack C.J., Twigger R., Buelens O., Hughes C.F.M., Lade S. et al. The efficacy of methotrexate for lymphomatoid papulosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015; 72(6): 1088–1090, doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.001. Erratum in: J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015; 73(3): 532.
47.
Champagne T., Walsh S. Mycophenolic acid for lymphomatoid papulosis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2013; 17(5): 332–334, doi: 10.2310/7750.2013.12111.
48.
Duvic M., Tetzlaff M.T., Gangar P., Clos A.L., Sui D., Talpur R. Results of a phase II trial of brentuximab vedotin for CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and lymphomatoid papulosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015; 33(32): 3759–3765, doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.3787.
Udostępnij
Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach, jako Operator Serwisu annales.sum.edu.pl, przetwarza dane osobowe zbierane podczas odwiedzania Serwisu. Realizacja funkcji pozyskiwania informacji o Użytkownikach i ich zachowaniu odbywa się poprzez dobrowolnie wprowadzone w formularzach informacje, zapisywanie w urządzeniach końcowych plików cookies (tzw. ciasteczka), a także poprzez gromadzenie logów serwera www, będącego w posiadaniu Operatora Serwisu. Dane, w tym pliki cookies, wykorzystywane są w celu realizacji usług zgodnie z Polityką prywatności.
Możesz wyrazić zgodę na przetwarzanie danych w tych celach, odmówić zgody lub uzyskać dostęp do bardziej szczegółowych informacji.
Możesz wyrazić zgodę na przetwarzanie danych w tych celach, odmówić zgody lub uzyskać dostęp do bardziej szczegółowych informacji.